We, who live in a start up environment, often we deal with uncertainties. The changes occur quickly and we must always be prepared to match these changes with agility. These changes can often affect the company’s business, making it necessary to a constant monitoring of the business model so that it is always aligned to the reality of the organization. In today’s post we present a tool to support the mapping of a business model, the Business Model Canvas.
According to the book “Business Model Generation” …
“Business model it is a description logic by which an organization creates, delivers and captures value.”
It is a model that identifies and describes all of the elements necessary for the operation of the Organization in order to achieve their goals. There are several tools and techniques for the construction of a business model. Considering a start up, the idea is that to have a way to create this model in a simple and intuitive format and be able to explain the complexities of how the company generates value. This is the objective of the Business Model Canvas (BMC)!
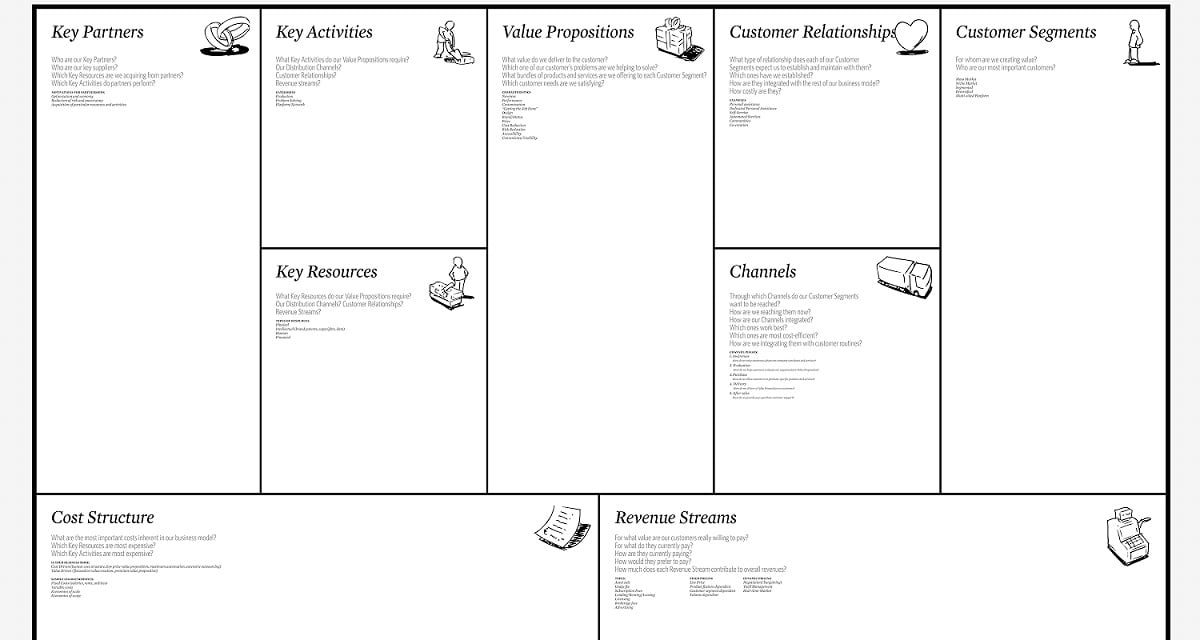
Proposed by Alexander Osterwalder, the BMC is a strategic management tool, consisting of a visual map that enables new business models or describe existing ones. It is a representation of the main elements involved in the operation of an organization. In picture below we have the image of the visual map of the BMC.
The BMC consists of 9 blocks described below:
- Customers: Is the audience to whom the organization wants to deliver value through its products and services. To succeed, the organization needs to identify what the public it want to meet. This audience can be segmented according to their needs and characteristics.
- Value Propositions: Is the set of products and services offered by the Organization to meet the needs of its customers. According to Alexander Osterwalder, the value proposition is what differentiates an company from its competitors.
- Channels: It is the set of ways by which the organization offers its products and services. An organization can offer their products and services through various channels, such as sales by phone, internet, consultants or physical stores, for example.
- Customer Relationship: It is the set of ways which the organization interacts with its customers. To succeed an organization needs to identify the kind of relationship that must maintain with its customer, according to their characteristics.
- Revenue Model: It is how the organization generates income from its customer. Are the ways to capture value from the company delivering value to their customers.
- Key Resources: It is the set of the necessary resources in order to generate value for the client. The elements needed to sustain and support the business. Resources can be people, machines, money, etc.
- Main activities: The main activities of the organization for the implementation of its proposals.
- Partnerships: Firm organization alliances in order to reduce the costs and risks and to be able to focus on its core business.
- Cost structure: Are the consequential costs of the resources used in the operation of the business.
Now that we know a little more about this map, we will understand how to fill it. In order to fit the business model using the table presented above, we can play it on a white board, for example, or in some other way that everyone involved in the construction of business model can work collaboratively. For filling the blocks can be used post-its, that are easy handling, especially when you need to make any changes on the map.
We can divide the board into two main regions: the one on the right side, which contains the most subjective elements and more related to the characteristics of the client; and the one on the left side that contains the logical elements, related to the structure of the organization. It is recommended that the map be filled from right to left. Thus, the construction of the structure of the organization is driven by the characteristics and needs of customers.
Then the map start by filling out the Customer block, trying to identify to whom they want to generate value and who are the potential customers of the organization. Then fill out the Value Propositions block, seeking to map the proposals that meet the needs of customers in order to achieve the goals of the organization. Once the Customer and Value Propositions blocks are filled, we left for the fill of the Channel block, identifying the means by which the value will be delivered to customers. Then we left for the fill of the block of customer relationships, identifying the ways in which the Organization must relate to their customers to strengthen the client’s involvement with the business. Finalizing the right side, fill the Revenue Model, mapping the ways to generate revenue from the suggested value.
Starting to the left of the picture, start by filling out the Main Resources block, identifying the resources necessary for the operation of the business. Then fill out the block of Main Activities, identifying all activities necessary to produce the value propositions and keep the channels and relationships. Continuing, fill out the block of the partners, identifying partnerships that can participate with resources or activities. Finally, fill in the cost structure, identifying all the monetary consequences of the means used for the operation of the business, finalizing the map.
Thus, the BMC application simplifies and can facilitate the understanding of an organization’s business, because it concentrates all the elements involved in the working of an organization in a same frame and can be easily manipulated. Considering an environment of uncertainty, the BMC figure as a very useful tool not only for creating but mainly for maintenance of a company’s business model.









Olá Pessoal,
Para quem usa o Business Model Canvas, tenho um produto bem legal!
http://www.thinkvinil.com/#!landing-page-2/c1wdo
Obrigada.